Judging Dairy Cattle
Dairy Cattle Judging
The physical conformation of a dairy cow is evaluated on four (4) categories:
- Dairy Strength - 25 points
- Rear Feet and Legs - 20 points
- Udder - 40 points
- Frame - 15 points
Dairy Strength
A cow that excels in dairy strength will have:
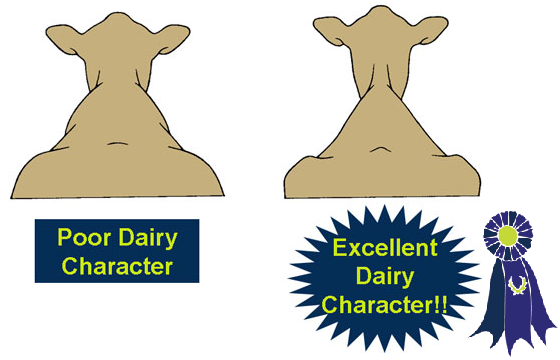
- A feminine head.
- A long, lean neck.
- Sharp and angular withers.
- A long barrel.
- A lot of space between her ribs.
- Ribs that are flat in shape (not round).
- A flat (not round) conformation in the part of her legs between the hocks and dew claws.
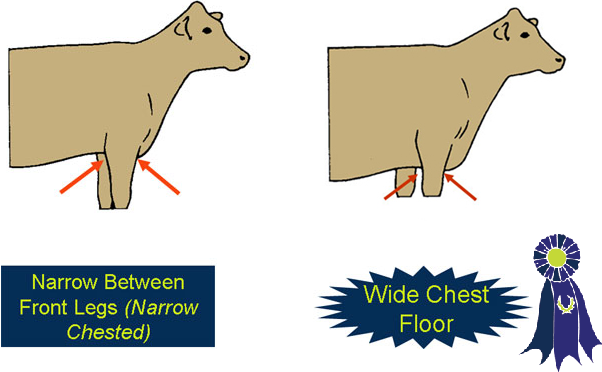
- Wide through the chest floor.
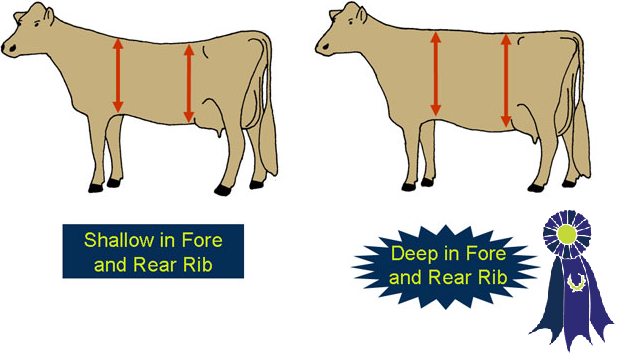
- Deep in the fore and rear rib.
- Long in the rib (barrel) region.
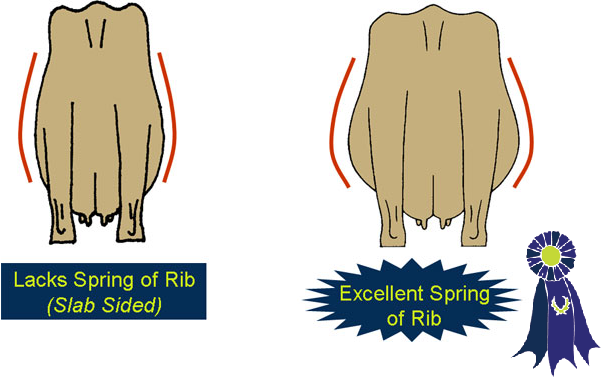
- Very wide through the rib (lots of spring of rib).
Dairy Strength
A cow that lacks dairy strength may have:
- A short, coarse head.
- A short, thick neck.
- Round withers.
- A short barrel.
- Little space between her ribs.
- Round ribs.
- Round lower legs.
- Narrow between the front legs (narrow chested).
- Shallow in the fore and rear rib.
- Short in the rib (barrel) region.
- Narrow through the ribs (slab sided).
Dairy Strength
- Chest Width -
- Fore and Rear Rib Depth -
- Spring of Rib -
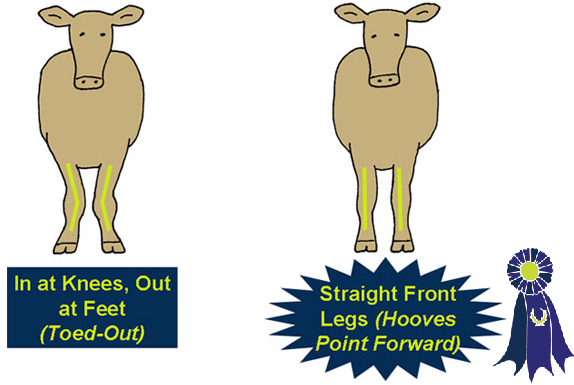
Front Feet and Legs
A cow with correct front feet and legs will have:
- Hooves which point straight forward.
- Straight front legs which set square with her body.
A cow which is not correct in the front feet and legs may have:
- Hooves with toes that turn in or out.
- Crooked front legs.
Front Feet and Legs
- Front Legs (Front View) -
Rear Feet and Legs
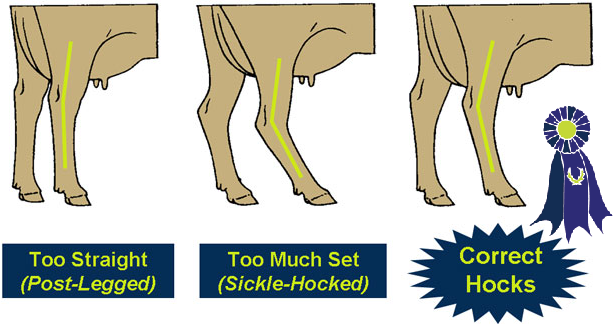
A cow with correct rear feet and legs will have:
- Hind legs that are placed squarely underneath her when she stands.
- A moderate set (curve) to her hocks.
- Clean hocks.
- Short, strong pasterns.
- A deep heel.
- A steep foot angle.
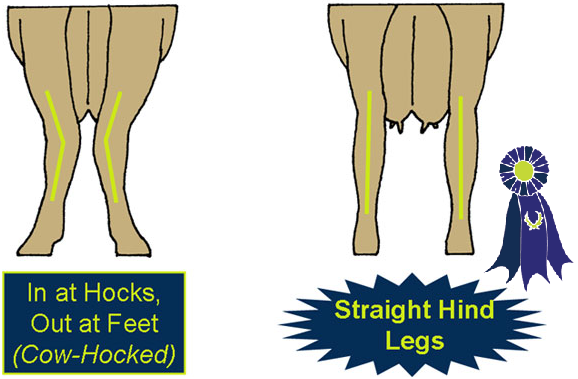
- Straight hind legs when viewed from the rear.
- An easy, smooth stride when she walks.
Rear Feet and Legs
A cow with incorrect rear feet and legs may have:
- Hid legs that attach too far back on the rump (thurl placement too far back).
- Too much set to the hocks (sickle-hocked) or hocks that are too straight (post-legged).
- Swelling or puffiness in the hocks.
- Weak pasterns.
- Heels that are too shallow.
- A low foot angle.
- Hocks that are in when viewed from the rear (cow-hocked).
- A restricted, uncomfortable stride.
Rear Feet and Legs
- Hocks -
Rear Feet and Legs
- Foot Angle and Depth of Heel -
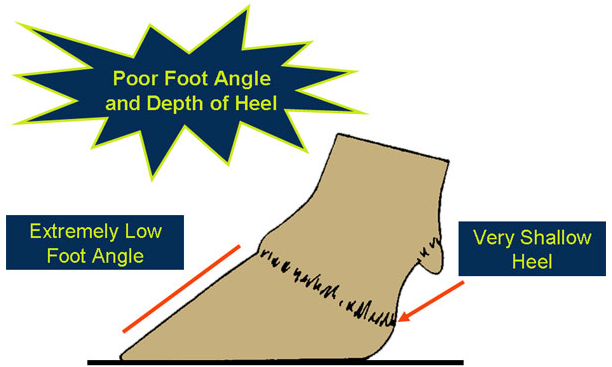
Rear Feet and Legs
- Foot Angle and Depth of Heel -
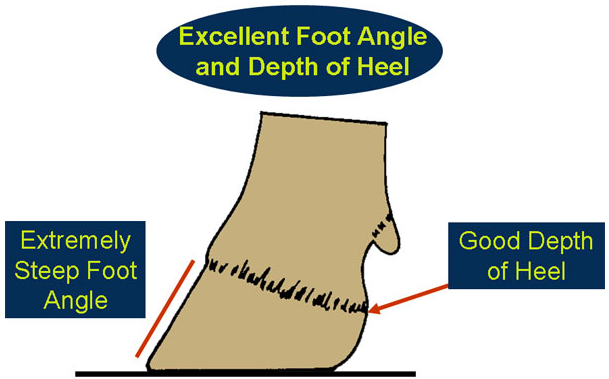
Rear Feet and Legs
- Hind Legs (Rear View) -
Udder Conformation
A cow which excels in udder conformation will have:
- An udder that is appropriate in size and capacity relative to the cow's age and number of lactations.
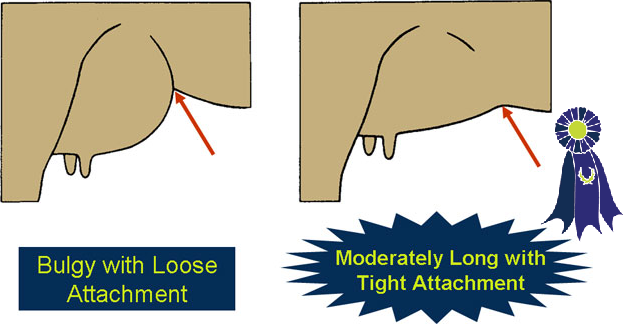
- A moderately long for udder that blends well into the body wall.
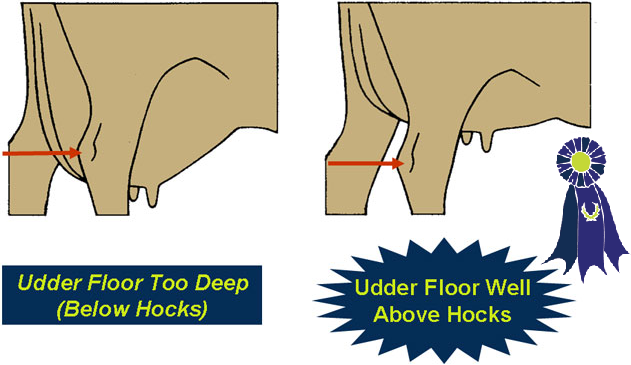
- A level udder floor, with the udder floor well above the hocks.
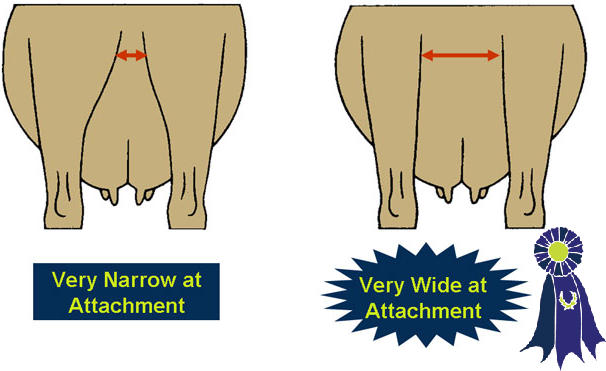
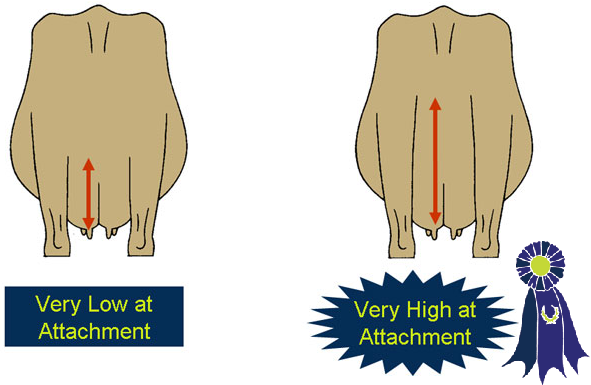
- A full and wide rear udder.
- A high and wide rear udder attachment.
- Balanced quarters.
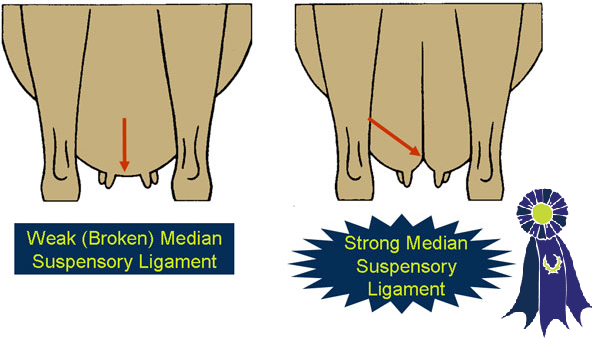
- Evidence of a strong median suspensory ligament.
- A lot of veining in the udder.
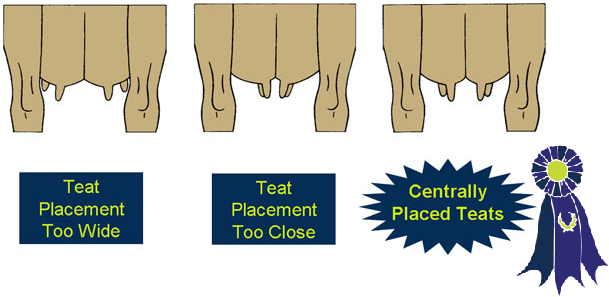
- Teats which are moderate in size and length, squarely placed under the quarter and perpendicular to the ground.
Udder Conformation
A cow which does not excel in udder conformation may have:
- A bulgy for udder.
- A loose for udder attachment.
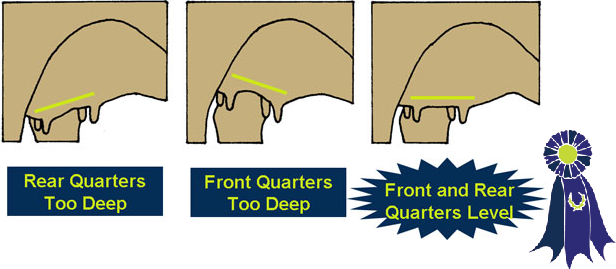
- Too much slope to the udder floor, or reverse tilt to the udder floor.
- An udder floor below the hocks.
- A flat and narrow rear udder.
- A low and narrow rear udder attachment.
- Unbalanced quarters.
- A weak median suspensory ligament.
- Teats that are not the correct size or shape.
- Front teats that are too wide.
- Front teats that strut out.
- Rear teats that are too close.
Udder Conformation
- Fore Udder -
Udder Conformation
- Udder Depth -
Udder Conformation
- Udder Tilt -
Udder Conformation
- Rear Udder Width -
Udder Conformation
- Rear Udder Height -
Udder Conformation
- Median Suspensory Ligament -
Udder Conformation
- Teat Placement -
Frame
A cow which is correct in her frame will be:
- Tall.
- Long from her muzzle to her pins.
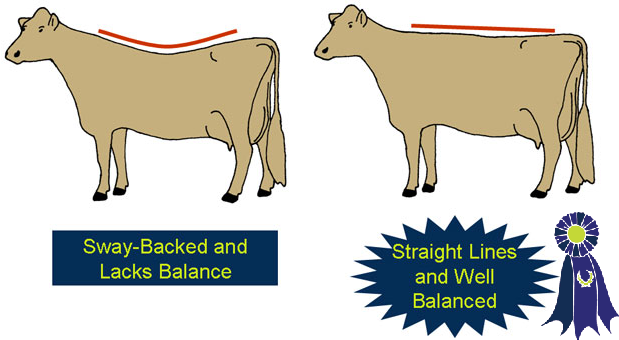
- Straight in her lines.
- Balanced and smoothly put together.
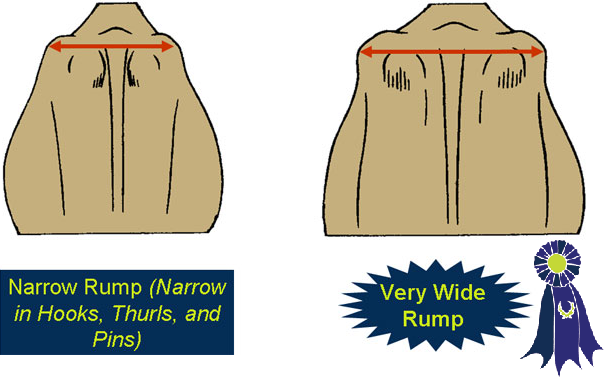
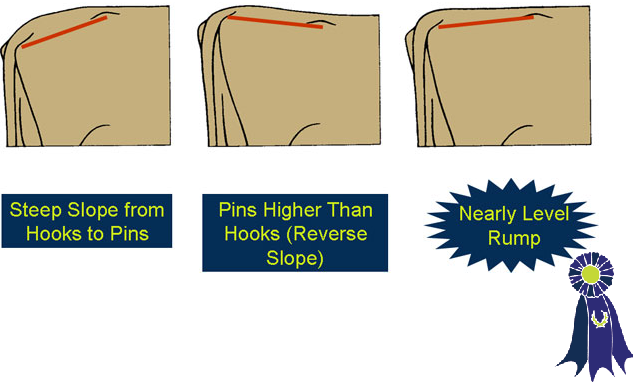
- Long and wide in her rump with a moderate amount of slope from the hooks to the pins.
Frame
A cow which is not correct in her frame may be:
- Low set.
- Short from her muzzle to her pins.
- Sway backed.
- Rough at the shoulder.
- Steep sloped from the hooks to the pins.
- Reverse tilted in the rump with the pins being higher than the hooks.
- Narrow in the hooks, thurls, and pins.
Frame
- Straightness of Design -
Frame
- Rump Width -
Frame
- Rump Slope -
Judge Dairy Cattle
When judging a class of four dairy animals, your assignment is to:
- First, evaluate what is correct and incorrect about the conformation of each animal.
- Second, rank the class based on their overall conformation.
- Most correct animal goes 1st
- Second most correct animal goes 2nd
- Third most correct animal goes 3rd
- Least correct animal goes 4th
Final Tips for Judging Dairy Cattle

- Remember the four important physical conformation categories.
- Know what "correct" looks like.
- Look at lots of dairy cattle.
- Practice your judging skills.

